The VDR appears to play an important role
in hair follicle cycling by regulating the growth cycle, inducing the development of mature anagen hairs and enabling
stem cells in the bulge to replicate. The ligand-independent actions of the VDR would seem to imply that vitamin D
is not necessary for the hair growth functions, however,research reveals a strong association between serum levels
of 1,25(OH) vitamin D, certain gene polymorphisms, and VDR expression.
To control for gene variations (polymorphisms) in the VDR and vitamin D metabolism, a study in monozygotic twins
was performed while studying vitamin D supplementation and its influence on VDR expression.
In the study group,supplementation with cholcalciferol (vitamin D3) 2,000 IU
× 60 days was found to not only significantly increase serum25(OH) vitamin D by 65%, but it markedly increased the
gene expression of VDR’s as well.
Pics of start at left- 6 months in center-12 months at right
Attachments
-
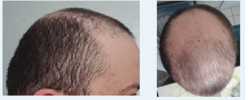 Screenshot 2024-12-31 at 16-53-03 Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss A Case Report and Review ...png80.3 KB · Views: 38
Screenshot 2024-12-31 at 16-53-03 Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss A Case Report and Review ...png80.3 KB · Views: 38 -
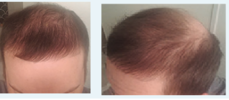 Screenshot 2024-12-31 at 16-52-48 Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss A Case Report and Review ...png79 KB · Views: 39
Screenshot 2024-12-31 at 16-52-48 Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss A Case Report and Review ...png79 KB · Views: 39 -
 Screenshot 2024-12-31 at 16-53-19 Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss A Case Report and Review ...png103 KB · Views: 38
Screenshot 2024-12-31 at 16-53-19 Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss A Case Report and Review ...png103 KB · Views: 38
Last edited:


